文摘
国际关注可持续发展挑战我们行动的内在联系我们的经济,社会和环境,导致生物多样性的增加确认的重要性。本文论述了生物多样性的方式的宽度可以支持可持续发展。它使用可持续发展目标(西班牙)为基础探索科学证据的好处由生物多样性。它关注论文提供的例子生物多样性如何组件(即生态系统、物种和基因)直接提供好处,可能导致个别西班牙的成就。它还考虑如何实现生物多样性的直接贡献一些西班牙可能间接支持其他西班牙的成就,生物多样性并不直接贡献。的属性(例如,多样性,丰富或成分)生物多样性的组件影响交付的好处也提出,论文回顾了所描述的。虽然承认潜在的负面影响和权衡不同的好处,这项研究得出结论,生物多样性可能导致所有西班牙的实现。
这是一个预览的订阅内容,通过访问你的机构
相关的文章
开放获取文章引用这篇文章。
检查连接在多个可持续发展成果:生产安全网计划增加田间agrobiodiversity吗?
环境、发展和可持续性开放获取2023年4月25日
干旱灾害和利益相关者的看法:解开干旱严重程度之间的联系,认为影响,防范和管理
中记录开放获取2023年4月03
栖息地的功能的新指标揭示高低估风险的权衡之间的可持续发展目标:野生驯鹿和水力发电
中记录开放获取2023年2月09
访问选项
访问其他自然组合期刊性质和54
得到自然+,请求书在线访问订阅
29.99美元/ 30天
取消任何时候
订阅本杂志
收到12个数字问题和在线访问的文章
每年119.00美元
只有9.92美元的问题
本文租或购买
价格不同的文章类型
从1.95美元
来39.95美元
价格可能受当地税收计算在结帐
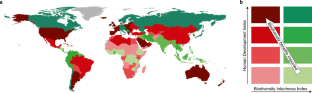
底图:Esri DeLorme出版社有限公司
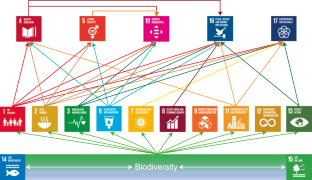
联合国/西班牙)。
引用
世界环境与发展委员会我们共同的未来(牛津大学出版社,1987)。
Cardinale, b . j . et al .生物多样性损失及其对人类的影响。自然486年59 - 67 (2012)。回顾二十年的研究生物多样性丧失如何影响生态系统功能和提供商品和服务。
Norstrom诉et al。三个必要条件在人类世建立有效的可持续发展目标。生态。Soc。198 (2014)。
Costanza, r . et al。二十年的生态系统服务:我们走了多远,我们还需要走多远?Ecosyst。服务公司。28硕士论文(2017)。
Blicharska, m . et al .深浅的灰色挑战文化生态系统服务概念的实际应用。Ecosyst。服务公司。2355 - 70 (2017)。
生物多样性和可持续发展:技术报告(环境署,2016)。
的附属机构在科学、技术和技术建议21会议:生物多样性和2030年的可持续发展议程(SBSTTA, 2017)。
木材、单反et al。蒸馏作用可持续发展的生态系统服务的目标。Ecosyst。服务公司。29日,70 - 82 (2018)。
舒尔茨,M。,Tyrrell, T. D. & Ebenhard, T.2030年议程和生态系统之间的联系——一篇论文在爱知生物多样性目标和可持续发展的目标(SwedBio斯德哥尔摩应变中心,2016)。
总结为决策者的区域生物多样性和生态系统服务评估报告欧洲和中亚地区的政府间生物多样性和生态系统服务科学政策平台(IPBES, 2018)。
总结为决策者的非洲区域生物多样性和生态系统服务评估报告政府间生物多样性和生态系统服务科学政策平台(IPBES, 2018)。
总结为决策者区域生物多样性和生态系统服务评估报告的美洲政府间生物多样性和生态系统服务科学政策平台(IPBES, 2018)。
总结为决策者区域生物多样性和生态系统服务评估报告的亚洲和太平洋地区政府间生物多样性和生态系统服务科学政策平台(IPBES, 2018)。
总结为决策者的全球生物多样性和生态系统服务评估报告政府间生物多样性和生态系统服务科学政策平台(IPBES, 2019)。
(goldman Sachs), j . d . et al .生物多样性保护和千禧年发展目标的实现。科学325年,1502 - 1503 (2009)。
l·卡拉斯科R。陈,J。,McGrath, F. L. & Nghiem, L. T. P. Biodiversity conservation in a telecoupled world.生态。Soc。2224岁(2017年)。
刘建,一个集成框架,实现可持续发展目标。生态。经济学。Soc。法国国家统计局J。1,17岁(2018)。研究引入一个集成耦合实现可持续发展目标的框架。
Syrbe R.-U。& Walz美国空间指标的评估生态系统服务:提供、受益和连接区域和景观指标。生态。印度的。21,80 - 88 (2012)。
青春痘,C。,Graves, R. A. & Turner, M. G. How do land-use legacies affect ecosystem services in United States cultural landscapes?Landsc。生态。32,2205 - 2218 (2017)。
奥尼尔,公元前et al。联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会气候变化风险的理由。Nat,爬。改变728-37 (2017)。
Essl发表,f . et al .历史遗产积累塑造未来的生物多样性在全球变化迅速的时代。潜水员。Distrib。21,534 - 547 (2015)。
Raudsepp-Hearne, c . et al .解开环保主义者的悖论:为什么人类福祉提高生态系统服务降低吗?生物科学60,576 - 589 (2010)。
加斯顿,k . j .全球生物多样性的模式。自然405年,220 - 227 (2000)。
Mayer, a . L。,Kauppi, P. E., Angelstam, P. K., Zhang, Y. & Tikka, P. M. Importing timber, exporting ecological impact.科学308年,359 - 360 (2005)。
2016年人类发展报告:人类发展对每个人都(联合国开发计划署,2016)。
斯科尔斯,r . j . &比格斯r .生物多样性完整无缺索引。自然434年45-49 (2005)。
Lenzen, m . et al。国际贸易推动发展中国家的生物多样性的威胁。自然486年,109 - 112 (2012)。全球分析国际贸易对生物多样性的威胁。
莫兰,D。,Petersone, M. & Verones, F. On the suitability of input output analysis for calculating product-specific biodiversity footprints.生态。印度的。60,192 - 201 (2016)。
Angelsen et al。环境收入和农村生计:全球性竞争分析。世界开发。64年S12-S28 (2014)。
阿卜杜拉,a·n·M。斯泰西,N。,Garnett, S. T. & Myers, B. Economic dependence on mangrove forest resources for livelihoods in the Sundarbans, Bangladesh.森林政策经济学。64年15 - 24 (2016)。
Keesing f . et al .影响生物多样性的出现和传染病的传播。自然468年,647 - 652 (2010)。全面审查的证据表明,生物多样性流失影响传染病的传播。
Hartig, T。,Mang, M. & Evans, G. W. Restorative effects of natural-environment experiences.环绕。Behav。233-26 (1991)。
乌尔里希,r . s .视图通过一个窗口可能会影响康复手术。科学224年,420 - 421 (1984)。
van den博世,m &唱歌,a . o .城市自然环境作为自然解决方案改进公共卫生系统回顾的评论。环绕。Res。158年,373 - 384 (2017)。系统回顾自然健康的影响的解决方案。
Veitch j . et al .公园的可用性和身体活动,电视,和超重和肥胖的女性:结果来自澳大利亚和美国。健康的地方38,96 - 102 (2016)。
Hanski et al。环境生物多样性,人类微生物群,和过敏都是相互关联的。Proc。《科学。美国109年,8334 - 8339 (2012)。
冯,x问:& Astell-Burt t是社区绿地预防儿童哮喘之间的关联,邻居交通量和缺乏区域安全吗?4447年澳大利亚孩子的多层次分析。Int。j .包围。公共卫生》14543 (2017)。
Cipriani, j . et al .系统回顾的园艺疗法对残疾人心理健康状况的影响。Occup。其他。表示“状态”。健康3347 - 69 (2017)。
保安族,g . b .森林和气候变化:气候营力,反馈,和森林的好处。科学320年,1444 - 1449 (2008)。
Griscom, b . w . et al .自然气候解决方案。Proc。《科学。美国114年,11645 - 11650 (2017)。识别和量化研究自然气候变化解决方案。
约翰逊,c, n . et al。生物多样性损失,人类世的保护反应。科学356年,270 - 274 (2017)。
Gamfeldt, l . et al .更高水平的多种生态系统服务在森林树种。Commun Nat。41430 (2013)。
刘,C . l . C。,Kuchma, O. & Krutovsky, K. V. Mixed-species versus monocultures in plantation forestry: development, benefits, ecosystem services and perspectives for the future.水珠。生态。Conserv。15e00419 (2018)。
琼斯,h P。,Hole, D. G. & Zavaleta, E. S. Harnessing nature to help people adapt to climate change.Nat,爬。改变2,504 - 509 (2012)。
Pramova E。,Locatelli, B., Djoudi, H. & Somorin, O. A. Forests and trees for social adaptation to climate variability and change.电线爬。改变3,581 - 596 (2012)。
布洛克,a & Acreman m .湿地的水文循环的作用。二聚水分子。地球系统。科学。7,358 - 389 (2003)。
法利,k。,Jobbágy, E. G. & Jackson, R. B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: a global synthesis with implications for policy.水珠。改变医学杂志。11,1565 - 1576 (2005)。
托马斯,h &尼斯贝特认为,t .评估洪水泛滥平原林地上流动的影响。水环境。J。21,114 - 126 (2007)。
昆廷,j . N。,Edwards, G. M. & Morgan, R. P. C. The influence of vegetation species and plant properties on runoff and soil erosion: results from a rainfall simulation study in south east Spain.土地使用等内容。13,143 - 148 (1997)。
Gedan, k B。,Kirwan, M. L., Wolanski, E., Barbier, E. B. & Silliman, B. R. The present and future role of coastal wetland vegetation in protecting shorelines: answering recent challenges to the paradigm.爬。改变106年第七至第二十九页(2011)。
布兰登,c . M。,Woodruff, J. D., Orton, P. M. & Donnelly, J. P. Evidence for elevated coastal vulnerability following large-scale historical oyster bed harvesting.地球上冲浪。的过程。Landf。41,1136 - 1143 (2016)。
欧阳,x G。李,美国Y。,Connolly, R. M. & Kainz, M. J. Spatially-explicit valuation of coastal wetlands for cyclone mitigation in Australia and China.科学。代表。83035 (2018)。
纳瓦兹,R。,McDonald, A. & Postoyko, S. Hydrological performance of a full-scale extensive green roof located in a temperate climate.生态。Eng。82年,66 - 80 (2015)。
巴,C。,Cameira, M. D., Valente, F., de Carvalho, R. C. & Paco, T. A. Wet season hydrological performance of green roofs using native species under Mediterranean climate.生态。Eng。102年,596 - 611 (2017)。
Vijayaraghavan k .绿色屋顶:一个关键组件的作用,综述利益,限制和趋势。更新。维持。能源牧师。57,740 - 752 (2016)。
黄:h . et al .屋顶花园的影响在新加坡商业建筑的能源消耗。能源建设。35,353 - 364 (2003)。
吸气,k l . &罗d . b .广泛的可持续发展绿色屋顶的作用。Hortscience41,1276 - 1285 (2006)。
郭,z W。,Zhang, L. & Li, Y. M. Increased dependence of humans on ecosystem services and biodiversity.《公共科学图书馆•综合》5e13113 (2010)。
Balmford, et al。全球视角自然旅游的趋势。公共科学图书馆杂志。7e1000144 (2009)。
边缘、大肠等。绿色的瀑布:回顾生态系统适应在城市地区。水珠。环绕。Change-Hum。Dimens政策。36,111 - 123 (2016)。
Trepel, m .评估的成本效益的净水功能的湿地环境规划。生态。复杂。7,320 - 326 (2010)。
沈,y Q。,Liao, X. C. & Yin, R. S. Measuring the socioeconomic impacts of China’s Natural Forest Protection Program.环绕。Dev,经济学。11,769 - 788 (2006)。
琐碎,洛杉矶将农业生物多样性和食品安全:agrobiodiversity对可持续农业的重要作用。Int,等于off。76年,283 - 297 (2000)。
达菲,j·E。,Godwin, C. M. & Cardinale, B. J. Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity.自然549年,261 - 265 (2017)。
虫,b . et al,生物多样性的丧失对海洋生态系统服务的影响。科学314年,787 - 790 (2006)。一个全球生产力的分析揭示生物多样性的重要性和海洋生态系统的稳定。
Winfree,发明r . et al .物种周转率促进农作物授粉的蜜蜂多样性的重要性在区域尺度。科学359年,791 - 793 (2018)。
克莱恩,a . m . et al。对世界作物传粉者改变景观的重要性。Proc。皇家Soc。B-Biol。科学。274年,303 - 313 (2007)。
奥布赖恩,c . j . et al .食肉动物和食腐动物对人类福利的贡献。Nat,生态。另一个星球。2,229 - 236 (2018)。掠食者的角色的全面审查为人们提供一系列的福利。
哈达德:M。,Crutsinger, G. M., Gross, K., Haarstad, J. & Tilman, D. Plant diversity and the stability of foodwebs.生态。列托人。1442-46 (2011)。
Chaplin-Kramer, r & Kremen c .害虫防治实验表明复杂性在景观和地方尺度的好处。生态。达成。22,1936 - 1948 (2012)。
贝尔,j·S。,van Lenteren, J. C. & Bigler, F. Biological control and sustainable food production.费罗斯。反式。皇家Soc。B-Biol。科学。363年,761 - 776 (2008)。
Motlhanka d . m . & Makhabu s . w .药用和食用的野果植物博茨瓦纳新兴新作物的机会。j .地中海植物Res。5,1836 - 1842 (2011)。
杰克逊,l . et al .生物多样性和农业sustainagility:从评估自适应管理。咕咕叫。当今。环绕。维持。2,80 - 87 (2010)。
Lachat, c . et al .膳食食品生物多样性和物种丰富度作为衡量营养饮食的质量。Proc。《科学。美国115年,127 - 132 (2018)。
弗林特,h·J。,Scott, K. P., Louis, P. & Duncan, S. H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health.Nat,启杂志。乙醇。9,577 - 589 (2012)。
Belkaid y &手,t . w .微生物群的免疫和炎症的作用。细胞157年,121 - 141 (2014)。
Atanasov, a . g . et al .药物活性植物的天然产物的发现和补给:复习一下。Biotechnol。睡觉。33,1582 - 1614 (2015)。
阿尔维斯,r . r . n和阿尔维斯,h . n .动物区系的药店:动物性的补救措施在拉丁美洲的传统药物使用。j . Ethnobiol。Ethnomed。79 (2011)。
金,c, D。,Fernald, L. C. H., Brashares, J. S., Rasolofoniaina, B. J. R. & Kremen, C. Benefits of wildlife consumption to child nutrition in a biodiversity hotspot.Proc。《科学。美国108年,19653 - 19656 (2011)。
刘,L。,Guan, D. S. & Peart, M. R. The morphological structure of leaves and the dust-retaining capability of afforested plants in urban Guangzhou, South China.环绕。科学。Pollut。Res。19,3440 - 3449 (2012)。
Fuller, r。,Irvine, K. N., Devine-Wright, P., Warren, P. H. & Gaston, K. J. Psychological benefits of greenspace increase with biodiversity.医学杂志。列托人。3,390 - 394 (2007)。
赫德布洛姆,M。,Heyman, E., Antonsson, H. & Gunnarsson, B. Bird song diversity influences young people’s appreciation of urban landscapes.城市。城市绿色。13,469 - 474 (2014)。
卡梅隆,r·w·F。,Taylor, J. & Emmett, M. A Hedera green facade - energy performance and saving under different maritime-temperate, winter weather conditions.构建。环绕。92年,111 - 121 (2015)。
Lurie-Luke大肠产品和技术创新:生物仿生启发呢?Biotechnol。睡觉。32,1494 - 1505 (2014)。
卡拉乔洛,a, B。,Topp, E. & Grenni, P. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities. A review.j .制药。生物医学。肛交。106年技能(2015)。
Megharaj, M。,Ramakrishnan, B., Venkateswarlu, K., Sethunathan, N. & Naidu, R. Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: a critical perspective.环绕。Int。37,1362 - 1375 (2011)。
6、J。,Frey, S. D., Thiet, R. K. & Batten, K. M. Bacterial and fungal contributions to carbon sequestration in agroecosystems.土壤科学。Soc。点。J。70年,555 - 569 (2006)。
马丁,t . L。,Trevors, J. T. & Kaushik, N. K. Soil microbial diversity, community structure and denitrification in a temperate riparian zone.Biodivers。Conserv。8,1057 - 1078 (1999)。
Cardinale, b . j .生物多样性提高水质通过利基分区。自然472年,86 - 89 (2011)。
Kulshreshtha,。Agrawal, R。,Barar, M. & Saxena, S. A review on bioremediation of heavy metals in contaminated water.IOSR j .包围。科学。Toxicol。食品工艺。844-50 (2014)。
休伊特,d . g .沙丘的殖民化与滨草稳定后(Ammophila Arenaria)。j .生态。58,653 - 668 (1970)。
Di Minin E。弗雷泽,我。,Slotow, R. & MacMillan, D. C. Understanding heterogeneous preference of tourists for big game species: implications for conservation and management.动物Conserv。16,249 - 258 (2013)。
霍夫曼,a . a . & Sgro c . m .气候变化和进化适应。自然470年,479 - 485 (2011)。
鲁伊斯,k b . et al .藜麦生物多样性气候变化和可持续发展下的粮食安全。复习一下。阿格龙。维持。Dev。34,349 - 359 (2014)。
穆尼奥斯,N。刘,。菅直人,L。,Li, M.-W. & Lam, H.-M. Potential uses of wild germplasms of grain legumes for crop improvement.Int。j .摩尔。科学。18328 (2017)。
伯克,m . B。,Lobell, D. B. & Guarino, L. Shifts in African crop climates by 2050, and the implications for crop improvement and genetic resources conservation.水珠。环绕。Change-Hum。Dimens政策。19,317 - 325 (2009)。
实习,j . M。,Arnaud-Haond, S. & Duarte, C. M. What lies underneath: conserving the oceans’ genetic resources.Proc。《科学。美国107年,18318 - 18324 (2010)。
Swanson, t .北部经济的依赖在南方生物多样性:生物多样性信息。生态。经济学。17,1 - 8 (1996)。
大卫,B。,Wolfender, J. L. & Dias, D. A. The pharmaceutical industry and natural products: historical status and new trends.Phytochem。牧师。14,299 - 315 (2015)。
邓肯·g·J。,Brooksgunn, J. & Klebanov, P. K. Economic deprivation and early-childhood developments.孩子开发。65年,296 - 318 (1994)。
Victora, c . g . et al .孕产妇和儿童营养不良2 -孕产妇和儿童营养不良:影响成人健康和人力资本。《柳叶刀》371年,340 - 357 (2008)。
古德曼,J。,Hurwitz, M., Park, J. & Smith, J.热量和学习(国家经济研究局(National Bureau of Economic Research), 2018)。
科尔,l . B。,McPhearson, T., Herzog, C. P. & Russ, A. in城市环境教育评论(eds Russ a & Krasny m . e .) 261 - 270(康奈尔大学出版社,2017年)。
Kevany, k & Huisingh d .回顾进展赋权妇女在农村水资源管理决策过程。j .干净。刺激。6053 - 64 (2013)。
原产地、h·d·不文明的生物多样性在女性的手:如何创建粮食主权。亚洲j .女人的螺栓。19,148 - 161 (2013)。
Adekola, O。,Mitchell, G. & Grainger, A. Inequality and ecosystem services: the value and social distribution of Niger Delta wetland services.Ecosyst。服务公司。1242-54 (2015)。
Bogar, s &拜尔,k . m .绿色空间,暴力,和犯罪:系统回顾。创伤暴力虐待17,160 - 171 (2016)。
Schleussner, c F。盾,j·F。,Donner, R. V. & Schellnhuber, H. J. Armed-conflict risks enhanced by climate-related disasters in ethnically fractionalized countries.Proc。《科学。美国113年,9216 - 9221 (2016)。
Wischnath, g . & Buhaug h .大米或骚乱:在粮食生产和冲突严重程度在印度。政治Geogr。436 - 15 (2014)。
Aspergis:教育和民主:新证据来自161个国家。经济学。模型。71年59 - 67 (2018)。
麦科伊,D。,Chigudu, S. & Tillmann, T. Framing the tax and health nexus: a neglected aspect of public health concern.卫生经济学。政策法律12,179 - 194 (2017)。
Truong C。,Trück, S. & Mathew, S. Managing risks from climate impacted hazards – the value of investment flexibility under uncertainty.欧元。j .打开。Res。269年,132 - 145 (2018)。
Lectard p &鲁吉尔,大肠可以从无视发展中国家获得比较优势?距离的比较优势,出口多样化和复杂,专业化的动力。世界开发。102年,90 - 110 (2018)。
埃尔利希,p . r . &埃利希,a . h .《人口炸弹重提。电子。j .维持。Dev1第5 - 13,(2009)。
美国核管理委员会加拿大的森林。2017年年度报告(自然资源加拿大,加拿大森林服务,2017)。
拉科姆,O。古老的森林:在英国历史上,植被和使用(Castlepoint出版社,1983年)。
林业统计2017(林业委员会,2017)。
锏,通用汽车等。瞄准更高的生物多样性丧失的曲线弯曲。Nat。维持。1,448 - 451 (2018)。
Scharlemann, j . p . w . et al。全球目标映射:天人合一的格局。NERC贡献,洛克菲勒基金会和ESRC倡议,对可持续发展的地球:天人合一系统和联合国全球目标苏塞克斯大学(苏塞克斯可持续发展研究项目和联合国世界环境保护监测中心,2016)。
Wolosin, M。缓解气候变化的大规模造林:教训韩国、中国和印度(气候和土地利用联盟,2017)。
史密瑟斯,r . J。,Blicharska, M。&Laurance, W. F. Biodiversity boundaries.科学353年1108 (2016)。
纽伯尔德,t . et al。土地利用推动行星边界以外的陆地生物多样性?一个全球性的评估。科学353年,288 - 291 (2016)。
威尔逊,e . O。专辑里(哈佛大学出版社,1986)。
罗伊,d . et al .哪些组件或属性的生物多样性的影响维度的贫困?环绕。Evid。33 (2014)。
田中,N。,Sasaki, Y., Mowjood, M. I. M., Jinadasa, K. B. S. N. & Homchuen, S. Coastal vegetation structures and their functions in tsunami protection: experience of the recent Indian Ocean tsunami.Landsc。生态。Eng。3333-45 (2007)。
Mishra, et al。构建事前的弹性disaster-exposed山区:见解来自尼泊尔地震复苏。为名Int。j .灾难。风险原因。22,167 - 178 (2017)。
冯·Wettberg e·j·b·等。生态和基因组学的一个重要的作物野生相对是农业创新的前奏。Commun Nat。9649 (2018)。
特,t·H。每天,g . C。,Ehrlich, P. R. & Michener, C. D. Economic value of tropical forest to coffee production.Proc。《科学。美国101年,12579 - 12582 (2004)。
墙,d . H。,Nielsen, U. N. & Six, J. Soil biodiversity and human health.自然528年,69 - 76 (2015)。
贝克特,k . P。,Freer-Smith, P. H. & Taylor, G. Particulate pollution capture by urban trees: effect of species and windspeed.水珠。改变医学杂志。6,995 - 1003 (2000)。
拉赫曼·m·A。,Armson, D. & Ennos, A. R. A comparison of the growth and cooling effectiveness of five commonly planted urban tree species.城市Ecosyst。18,371 - 389 (2015)。
桑托斯et al。森林的作用减轻大气粉尘污染的影响在混合景观。环绕。科学。Pollut。Res。24,12038 - 12048 (2017)。
Detweiler, m . b . et al .园艺疗法:一个试点研究调节皮质醇水平和指标的物质欲望,创伤后应激障碍,抑郁,和退伍军人的生活质量。交错的。其他。健康医疗。2136-41 (2015)。
泰勒,m . S。,Wheeler, B. W., White, M. P., Economou, T. & Osborne, N. J. Research note: Urban street tree density and antidepressant prescription rates—A cross-sectional study in London, UK.Landsc。城市的计划。136年,174 - 179 (2015)。
约翰逊,C。,Schweinhart, S. & Buffam, I. Plant species richness enhances nitrogen retention in green roof plots.生态。达成。26,2130 - 2144 (2016)。
Meerburg, b . g . et al .地表水环境卫生和生物质生产在一个大型人工湿地在荷兰。Wetl。生态。等内容。18,463 - 470 (2010)。
奥斯本l . l . & Kovacic d . a .河岸植被缓冲带水质恢复和流管理。Freshw。医学杂志。29日,243 - 258 (1993)。
Verhoeven, j . t。,Arheimer B。,Yin, C. & Hefting, M. M. Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality.生态发展趋势。另一个星球。21,96 - 103 (2006)。
布鲁曼,k。,Freyberg, D. L. & Daily, G. C. Forest structure influences on rainfall partitioning and cloud interception: a comparison of native forest sites in Kona, Hawaii.阿格利司。对。Meteorol。150年,265 - 275 (2010)。
百利,R。,Drigo, R., Ghilardi, A. & Masera, O. The carbon footprint of traditional woodfuels.Nat,爬。改变5,266 - 272 (2015)。
艾略特,l . g . et al .建立bioenergy-focused microalgal文化收藏。藻Res。1,102 - 113 (2012)。
Heinsoo, K。融化我。,Sammul, M. & Holm, B. The potential of Estonian semi-natural grasslands for bioenergy production.阿格利司。Ecosyst。环绕。137年,86 - 92 (2010)。
Dornburg诉et al。生物能源的再现:关键因素在全球生物能源的潜力。能源环境。科学。3,258 - 267 (2010)。
王,z . H。,Zhao, X. X., Yang, J. C. & Song, J. Y. Cooling and energy saving potentials of shade trees and urban lawns in a desert city.达成。能源161年,437 - 444 (2016)。
帕默,c &迪法尔科,美国生物多样性,贫困,和发展。Oxf启经济学。政策2848 - 68 (2012)。
Tumusiime, d . m . & Vedeld, p .生物多样性保护当地居民受益吗?在严格的成本和收益在乌干达保护区。j .维持。对。34,761 - 786 (2015)。
Tzoulas, k . et al。促进城市生态系统和人类健康使用绿色基础设施:一个文献综述。Landsc。城市的计划。81年,167 - 178 (2007)。
先令,j . &洛根,j .绿化铁锈地带:绿色基础设施模型对美国萎缩城市规模。j。计划。Assoc。74年,451 - 466 (2008)。
贝拉尔迪的乳白色,U。,GhaffarianHoseini, A. H. & GhaffarianHoseini, A. State-of-the-art analysis of the environmental benefits of green roofs.达成。能源115年,411 - 428 (2014)。
Charlesworth, s M。,Perales-Momparler, S., Lashford, C. & Warwick, F. The sustainable management of surface water at the building scale: preliminary results of case studies in the UK and Spain.j .供水Technol.-Aqua》62年,534 - 544 (2013)。
葡萄园,d . et al .比较绿色和灰色基础设施使用寿命周期成本和环境影响:雨水花园案例研究在辛辛那提,哦。j。水Resour。Assoc。51,1342 - 1360 (2015)。
咚,X。,Guo, H. & Zeng, S. Y. Enhancing future resilience in urban drainage system: green versus grey infrastructure.水Res。124年,280 - 289 (2017)。
雷纳德·G。,Sudmeier-Rieux, K., Estrella, M. & Nehren, U.基于生态系统在实践中减少灾害风险和适应(Springer, 2016)。
豪斯曼,。Slotow, R。,Burns, J. K. & Di Minin, E. The ecosystem service of sense of place: benefits for human well-being and biodiversity conservation.环绕。Conserv。43,117 - 127 (2016)。
Blicharska, m & Mikusiński g .整合社会和文化意义巨大的老树的保护政策。Conserv。医学杂志。28,1558 - 1567 (2014)。
罗瑟勒姆,拿身份证的生态文化遗产和生物多样性:新兴范例在保护和规划。Biodivers。Conserv。24,3405 - 3429 (2015)。
Bhagwat s a &鲁特,c .神圣的树林:潜在的生物多样性管理。前面。生态。环绕。4,519 - 524 (2006)。
Kabisch, N。,van den Bosch, M. & Lafortezza, R. The health benefits of nature-based solutions to urbanization challenges for children and the elderly - a systematic review.环绕。Res。159年,362 - 373 (2017)。
生,B。Knez,我。,赫德布洛姆,M。&Sang, A. O. Effects of biodiversity and environment-related attitude on perception of urban green space.城市Ecosyst。20.37-49 (2017)。
尼尔森,a, B。,van den Bosch, M., Maruthaveeran, S. & van den Bosch, C. K. Species richness in urban parks and its drivers: a review of empirical evidence.城市Ecosyst。17,305 - 327 (2014)。
沙纳罕,d F。Fuller, r。布什,R。,Lin, B. B. & Gaston, K. J. The health benefits of urban nature: how much do we need?生物科学65年,476 - 485 (2015)。
McVittie,。,科尔,L。,Wreford, A., Sgobbi, A. & Yordi, B. Ecosystem-based solutions for disaster risk reduction: lessons from European applications of ecosystem-based adaptation measures.为名Int。j .灾难。风险原因。3242-54 (2018)。
Salick, j . et al .西藏圣地保存古老的树木和覆盖在喜马拉雅山东部的增长。Biodivers。Conserv。16,693 - 706 (2007)。
艾登,et al。有氧和厌氧真菌代谢组学的洞察力提高多环芳烃生物降解。真菌生物。牧师。31日,61 - 72 (2017)。
埃勒斯医生,。,Worm, B. & Reusch, T. B. H. Importance of genetic diversity in eelgrass Zostera marina for its resilience to global warming.3月Ecol.-Prog。爵士。355年1 - 7 (2008)。
威尔默,c . c &斯坦利·w·m·灰狼在气候变化缓冲区在黄石公园。公共科学图书馆杂志。3,571 - 576 (2005)。
史蒂芬,w . et al .行星边界:指导人类发展变化的星球上。科学347年,1259855 (2015)。
Stahel, w . r .循环经济。自然531年,435 - 438 (2016)。
Burch-Brown j . &阿切尔a以保护生物多样性。医学杂志。费罗斯。32,969 - 997 (2017)。
迈尔斯,N。,Mittermeier, R. A., Mittermeier, C. G., da Fonseca, G. A. B. & Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities.自然403年,853 - 858 (2000)。
肖,j . D。,Terauds, A., Riddle, M. J., Possingham, H. P. & Chown, S. L. Antarctica’s protected areas are inadequate, unrepresentative, and at risk.公共科学图书馆杂志。12e1001888 (2014)。
罗伊,D。,Elliott, J., Sandbrook, C. & Walpole, M. in生物多样性保护和减贫:探索一个链接的证据(eds Roe, d . et al。) 3-18(著名,2013)。
雷德福,k h &级、b . d .保护生物多样性的世界里使用。Conserv。医学杂志。13,1246 - 1256 (1999)。
作者信息
道德声明
相互竞争的利益
作者宣称没有利益冲突。
额外的信息
出版商的注意施普林格自然保持中立在发表关于司法主权地图和所属机构。
补充信息
补充信息
补充信息部分1 - 2、表和参考文献。1 - 4。
权利和权限
关于这篇文章
引用这篇文章
Blicharska, M。,Smithers, R.J., Mikusiński, G.et al。生物多样性对可持续发展的贡献。Nat维持2,1083 - 1093 (2019)。https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893 - 019 - 0417 - 9
收到了:
接受:
发表:
发行日期:
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893 - 019 - 0417 - 9
本文引用的
益处和风险的增量保护区规划在南大洋
自然的可持续性(2023)
蝙蝠能帮助造纸工业吗?一个评价桉树insect-related蝙蝠捕食
哺乳动物生物学(2023)
栖息地的功能的新指标揭示高低估风险的权衡之间的可持续发展目标:野生驯鹿和水力发电
中记录(2023)
检查连接在多个可持续发展成果:生产安全网计划增加田间agrobiodiversity吗?
环境、发展和可持续性(2023)
干旱灾害和利益相关者的看法:解开干旱严重程度之间的联系,认为影响,防范和管理
中记录(2023)
